A Framework for Crowd Management: The Importance of Cross-Entity and Cross-Functional Integration
By Konstantin Turuntcev, Managing Partner, Event Concept Consultancy QFZ LLC
Pic: Crowd Management, Safety and Control as one element
Crowd Management, Safety and Control nowadays is the “hot spot” topic among the people, who somehow are involved in the event industry: no matter if it is a concert or multi-sport event. There are different opinions on the definitions and approach itself; community speak about operations, new technologies – something that some people say may improve and help to avoid issues, challenges, disasters, human injuries, and deaths.
From studying the articles, conducting research and personal experience we realized the common patterns and challenges that arise during planning, implementation of the operations and the operations itself.
No matter which technologies we use, how properly we train the staff, how deep our knowledge in crowd management, safety and control - without integration of involved stakeholders in the process – everything can go wrong.
The Crowd Management Framework (here and after CMF) is the tool that helps to prevent risks that can be caused by large gatherings. CMF acts as a “RACI” (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) matrix defining the responsibilities among different stakeholders during planning and operations phases, providing a comprehensive chart of who is responsible, accountable, consulted, and informed every step of the way.
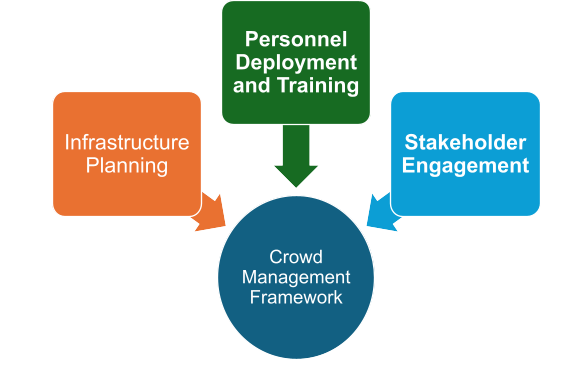
CMF is a tool uniting the stakeholders, defining their roles and contributions to ensure safe and secure environment. It covers the following aspects for the smooth operations:
Pic: Crowd Management Framework: key planning aspects
Infrastructure Planning (Venue architectural, permanent and temporary overlay, operational elements), such as: Clear and precise signage, optimized transport systems, pathway widths, throughput capacities of the pedestrian search and screening areas, turnstiles; distribution of concessions areas, toilets, etc.
Personnel Deployment and Training, such as: Well-equipped security, last mile and spectator services personnel, extensively trained to handle diverse scenarios, ensure efficient management and crowd control, manage queues, and understand diverse spectator profiles.
Stakeholder Engagement, such as: The framework involves various stakeholders crucial for executing security-focused activities across the spectator’s journey, like security personnel, transportation, and last-mile operations to venue management, ticketing, marketing, state security agencies, and international sports governing bodies.
CMF focused on 3 key operational regimes: ingress, circulation (spectators flows during the halftime), and egress. This framework aimed to synchronize efforts toward a single objective - ensuring strong safety, security and an exceptional experience for every spectator.
The more details we put in the CMF the clearer the picture of the operations and responsible parties we have, and the planning of the implementation of such frameworks puts all these stakeholders on one table to focus on the planning of the event.
Pic: Crowd Management Framework: key operational regimes
For example, you do your crowd management plan, but how and to whom you communicate the plan? Who is involved in the planning phase and discussions with you from the internal and external stakeholders? Here comes a Crowd Management Framework, that can help you to make sure that nothing is missed.
In conclusion, an integrated approach, Crowd Management Framework, is essential for ensuring the seamless delivery of safety, security, and service at large-scale sporting events. By learning from past experiences and embracing a collaborative mindset, event organizers can create an environment where people can enjoy the event safely and securely.